Introduction to Weakly Supervised Learning
Supervised Machine Learning relies on labelled data that consists of data and pairs of expected outputs. For example an image of dog that is labelled a dog. Supervised Machine Learning models are essentially mathematical models with parameters optimised according to a given criterion or what you would call a loss/error function that measures how the of a given model differs from an expected output. Curating the dataset on which the model is trained/tested requires manual effort of data labellers labelling every image for a given task. Some tasks are expensive to annotate and some are easier or we might have large well curated datasets for tasks that are easy to annotate.
Weakly supervised learning allows us to use the datasets which are easy to annotate to perform tasks that are more expensive to annotate. It could use another classifier to label the data or handcrafted domain knowledge. For, example from a dataset consisting of labelled pairs of image/label pairs is good for a classification task we could curate a dataset for object localisation and semantic segmentation and train a model for the same. Another example extending to text for sentimental analysis. We could take several rows of text and use if else statements to check if words that correspond to negative/positive sentiment are present and label the dataset accordingly. This leads to a dataset with noisy labels with which can learn a sentimental classifier. The intuition why this works is that most noisy labels have some learnable patterns. We must also ensure that the algorithm does not overfit to the noisy patterns. This can be done by curating a small dataset with correct labels which can be used as test set.
General Weakly Supervised Pipeline
- Label Dataset
- Use Noise labelled dataset to train classifier
- Relabel dataset
- Retrain classifier until convergence
In this blogpost I would like to introduce weak supervised learning and provide examples of how its done for object detection.
Object Detection
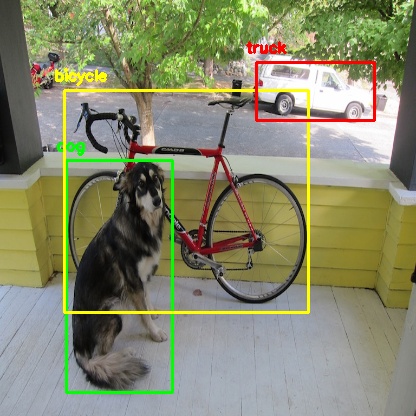
Object detection is the task of not only classifiying instances of given class but also specifying its bounding box location (task called localization). Annotating images with bounding boxes are more expensive as compared to anotating a single label for a image as in case for object classification. So instead we use a dataset consisting a pair of image/labels and train a classifier on it and use it to annotate bounding boxes for object detection.
There are several ways of leveraging weakly supervised learning to label datasets for segmentation and detection using an existing classifier. Annotating dataset for object detection has these steps
- Region Proposal
- Label regions
- Region Selection
- Label dataset
- Train Localization network
- Retrain localization network (Back to step 2)
I would explain these individual components in some detail
Region selection is done using selective max, sliding windows or edgebox. These regions are labelled by an classifier trained on classification task on classes contained in the image. The classifier is leveraged to label the regions. From the labelled regions the appropriate regions are selected for a given class. There are several stratergies to do so 1) choosing the region with maximum probability for given class 2) Choosing regions above certain probability. When approach 2 is choosen the regions can further be combined using some criteria such as intersection or distance between the regions. The dataset is further labelled. This labelled dataset is used to train a localization network learns to predict bounding boxes given an image. After the network is trained to convergence the dataset is relabelled using labels from localized network. This process is repeated for several iterations until convergence criteria is met.
The above motivates an naive approach of attaining weakly supervised learning, there are some approaches that perform steps 2-5 end to end which I will save for another blogpost. The end to end networks are trained only from classification labels but can also perform localization and detection.
Having motivated weakly supervised learning as a way of labelling data with less difficulty, its still far from use in production system to completely replace supervised learning and still an active research area. Some common issues being that it labels all closeby objects into a single boundig box or is biased towards the noise by the classifier.